WHO DISCOVERED CELL?
First Cells Seen in Cork
While the invention of the telescope made the Cosmos accessible to human observation, the microsope opened up smaller worlds, showing what living forms were composed of. The cell was first discovered and named by Robert Hooke in 1665. He remarked that it looked strangely similar to cellula or small rooms which monks inhabited, thus deriving the name. However what Hooke actually saw was the dead cell walls of plant cells (cork) as it appeared under the microscope. Hooke’s description of these cells was published in Micrographia. The cell walls observed by Hooke gave no indication of the nucleus and other organelles found in most living cells. The first man to witness a live cell under a microscope was Anton van Leeuwenhoek, who in 1674 described the algae Spirogyra. Van Leeuwenhoek probably also saw bacteria.

WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF CELL?


Differences Between Animal Cells and Plant Cells
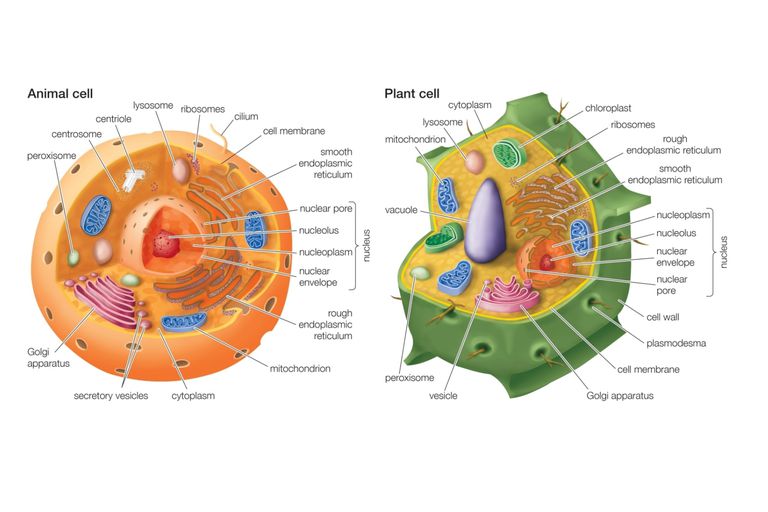
- Size: Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells. Animal cells range from 10 to 30 micrometers in length, while plant cells range from 10 and 100 micrometers in length.
- Shape: Animal cells come in various sizes and tend to have round or irregular shapes. Plant cells are more similar in size and are typically rectangular or cube shaped.
- Energy Storage: Animals cells store energy in the form of the complex carbohydrate glycogen. Plant cells store energy as starch.
- Proteins: Of the 20 amino acids needed to produce proteins, only 10 can be produced naturally in animal cells. The other so-called essential amino acids must be acquired through diet. Plants are capable of synthesizing all 20 amino acids.
- Differentiation: In animal cells, only stem cells are capable of converting to other cell types. Most plant cell types are capable of differentiation.
- Growth: Animal cells increase in size by increasing in cell numbers. Plant cells mainly increase cell size by becoming larger. They grow by absorbing more water into the central vacuole.
- Cell Wall: Animal cells do not have a cell wall but have a cell membrane. Plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose as well as a cell membrane.
- Centrioles: Animal cells contain these cylindrical structures that organize the assembly of microtubules during cell division. Plant cells do not typically contain centrioles.
- Cilia: Cilia are found in animal cells but not usually in plant cells. Cilia are microtubules that aid in cellular locomotion.
- Cytokinesis: Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm during cell division, occurs in animal cells when a cleavage furrow forms that pinches the cell membrane in half. In plant cell cytokinesis, a cell plate is constructed that divides the cell.
- Glyoxysomes: These structures are not found in animal cells, but are present in plant cells. Glyoxysomes help to degrade lipids, particularly in germinating seeds, for the production of sugar.
- Lysosomes: Animal cells possess lysosomes which contain enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules. Plant cells rarely contain lysosomes as the plant vacuole handles molecule degradation.
- Plastids: Animal cells do not have plastids. Plant cells contain plastids such as chloroplasts, which are needed for photosynthesis.
- Plasmodesmata: Animal cells do not have plasmodesmata. Plant cells have plasmodesmata, which are pores between plant cell walls that allow molecules and communication signals to pass between individual plant cells.
- Vacuole: Animal cells may have many small vacuoles. Plant cells have a large central vacuole that can occupy up to 90% of the cell’s volume.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE CELL?
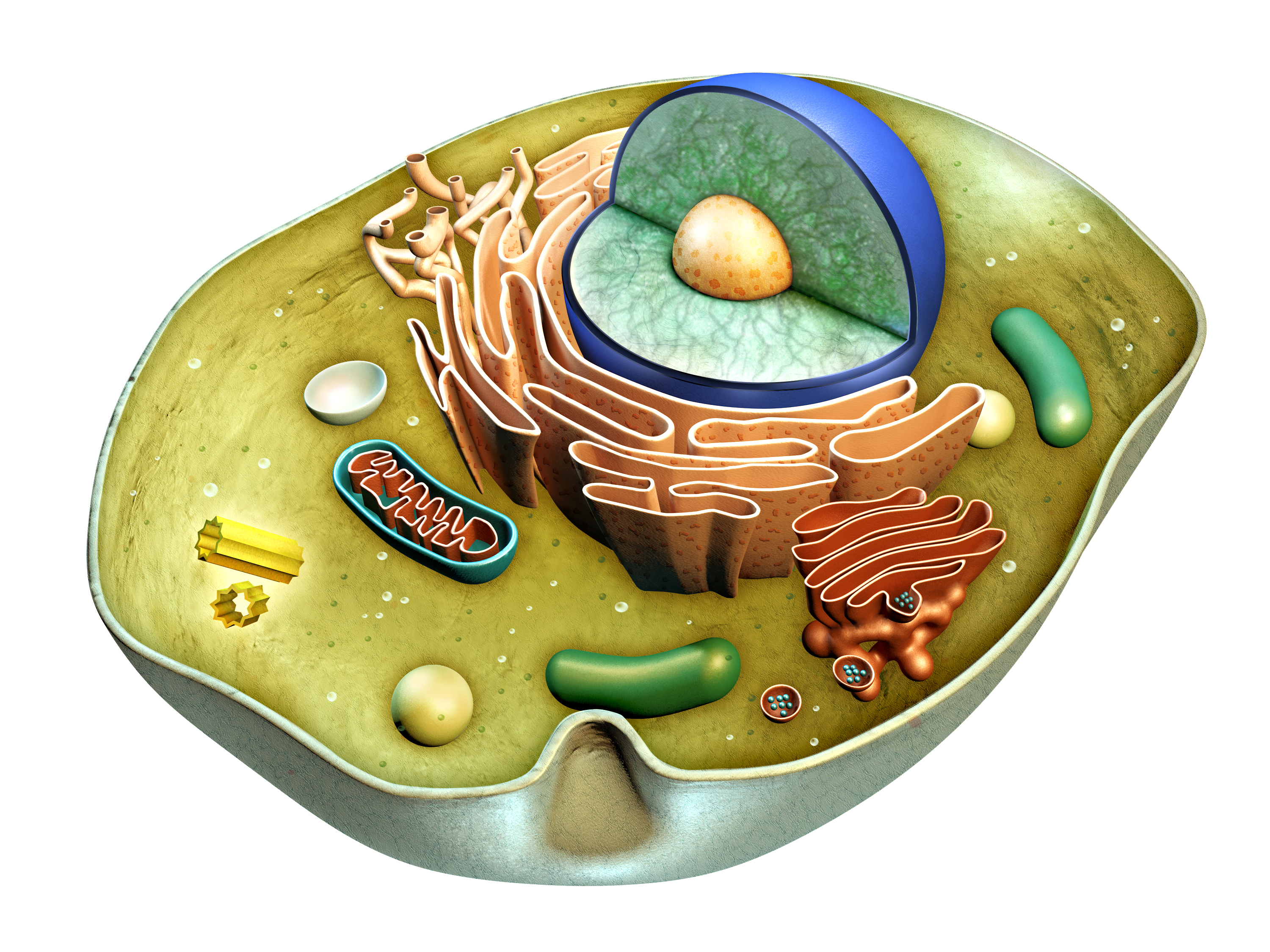
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
Cells have many parts, each with a different function. Some of these parts, called organelles, are specialized structures that perform certain tasks within the cell.
WHAT IS THE REFLECTION OF CELL FEATURES IN THE SOCIETY TODAY?
Cell is the basic unit of life, it reflects that cell is like a family which all the parts have functions even the smallest part in the family have function.
Vacuole is the storage of nutrients, it reflects that vacuole is like a factory in which all the product process in that factory.
Cell wall is the protection of the plant cell, it reflects that cell wall is to protect to the enemies around them
Mitochondria it is the power energy of the cell, it like a transformer which it store the energy.



